How to Evaluate Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that develop in the mouth, throat, larynx, nose, and sinuses. Early detection and evaluation are crucial for improving treatment outcomes. In this blog, we will explore the steps involved in assessing head and neck cancer, including signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and the role of a specialist. The ability to evaluate head and neck cancer accurately is essential for timely intervention and better prognosis.
Understanding the Risk Factors
Before delving into the evaluation process, it is important to understand the risk factors associated with head and neck cancer. Tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, and prolonged exposure to certain environmental toxins are key contributors. A thorough medical history is an essential first step in how to evaluate head and neck cancer because it helps the specialist assess the patient’s risk level and guide further investigation.
Recognizing Early Symptoms
Identifying symptoms early plays a pivotal role in the effective management of head and neck cancer. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent sore throat or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- A lump in the neck or throat
- Unexplained weight loss
- Ear pain or ringing in the ears
- Changes in voice
Understanding these warning signs is important when beginning the process of evaluating head and neck cancer. The earlier these symptoms are caught, the quicker the diagnosis and the more favorable the treatment outcomes.
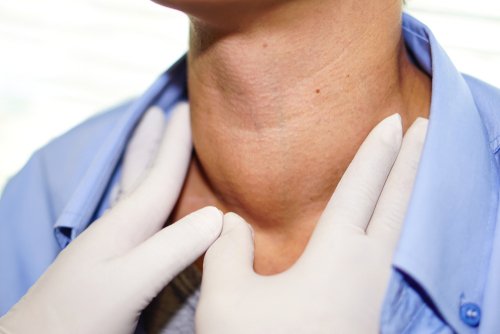
Comprehensive Physical Examination
The next step in how to evaluate head and neck cancer is a comprehensive physical examination. A thorough exam of the oral cavity, throat, nose, ears, and neck allows the physician to detect any abnormal growths or lumps. Physicians often use specialized tools like endoscopes to get a closer look at the tissues and detect any abnormalities. Palpation of the neck for swollen lymph nodes is another crucial aspect of this physical evaluation.
In some cases, the specialist may recommend a laryngoscopy or nasoendoscopy to gain a clearer view of the internal structures. These non-invasive procedures help in identifying tumors or growths that may not be visible externally.
Imaging Tests for Evaluation
Imaging plays a critical role in evaluating the extent of the disease. The most common imaging tests used to evaluate head and neck cancer include:
- CT Scans (Computed Tomography): Provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body, allowing the doctor to detect any abnormal masses or lymph node involvement.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Especially useful for examining soft tissues, and providing detailed information about the size and location of tumors.
- PET Scans (Positron Emission Tomography): Help to determine whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Ultrasound: Often used to assess lymph nodes in the neck, particularly for patients with thyroid or salivary gland cancers.
Each of these imaging modalities plays a specific role in the overall evaluation process. Depending on the suspected location of the cancer, your doctor may order one or more of these tests.
Biopsy for Confirmation
A biopsy is often necessary to confirm a diagnosis of head and neck cancer. During this procedure, a sample of tissue is collected and examined under a microscope to detect the presence of cancer cells. There are different types of biopsies used to evaluate head and neck cancer, including:
- Fine-needle aspiration Biopsy (FNAB): A thin needle is used to extract cells or fluid from a lump.
- Incisional or Excisional Biopsy: Involves removing part or all of a suspicious growth for examination.
- Endoscopic Biopsy: A small sample is collected using an endoscope during a minimally invasive procedure.
The biopsy results play a critical role in determining the next steps in treatment, whether surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of therapies will be required.
Evaluating the Stage of Cancer
Once cancer is confirmed, it is important to determine its stage. The staging process is a key aspect of how to evaluate head and neck cancer, as it provides information about the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. The TNM system is commonly used, which evaluates:
- T (Tumor): The main tumor’s size and extent
- N (Nodes): Whether cancer has spread to lymph nodes
- M (Metastasis): Whether cancer has spread to other parts of the body
Staging helps guide the treatment plan and offers insight into the patient’s prognosis.
Role of the Multidisciplinary Team
One of the essential aspects of how to evaluate head and neck cancer is the involvement of a multidisciplinary team. This team may include oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, pathologists, and other specialists who work together to assess the cancer and develop an individualized treatment plan. Each specialist contributes their expertise to ensure the most accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Importance of HPV Testing
For certain types of head and neck cancers, particularly those located in the oropharynx, HPV testing is a crucial part of the evaluation process. HPV-positive head and neck cancers tend to have a better prognosis and respond more favorably to treatment. Understanding whether the cancer is HPV-positive or negative can influence treatment decisions and outcomes.
Advanced Evaluation Techniques
In some cases, advanced evaluation methods like genetic testing or molecular profiling may be used to gain further insights into the tumor’s biology. These techniques are valuable in tailoring treatment plans and improving targeted therapy options.
Post-Diagnosis: Treatment Planning
Once the cancer has been thoroughly evaluated, the next step is formulating a treatment plan. The treatment options will vary depending on the type, location, and stage of the cancer. Common treatments for head and neck cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. The ultimate goal is to eliminate the cancer while preserving as much function as possible.
For patients undergoing treatment, regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are crucial to track the effectiveness of the therapy and detect any signs of recurrence.
Conclusion
Understanding how to evaluate head and neck cancer is vital for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and the successful treatment of this potentially life-threatening condition. From recognizing risk factors and early symptoms to undergoing comprehensive diagnostic tests, each step in the evaluation process plays a crucial role in improving outcomes. Working closely with a specialist and a multidisciplinary team ensures that patients receive the best possible care and guidance throughout their treatment journey.
For further information and to explore treatment options, visit Dr. Prateek Varshney’s website.